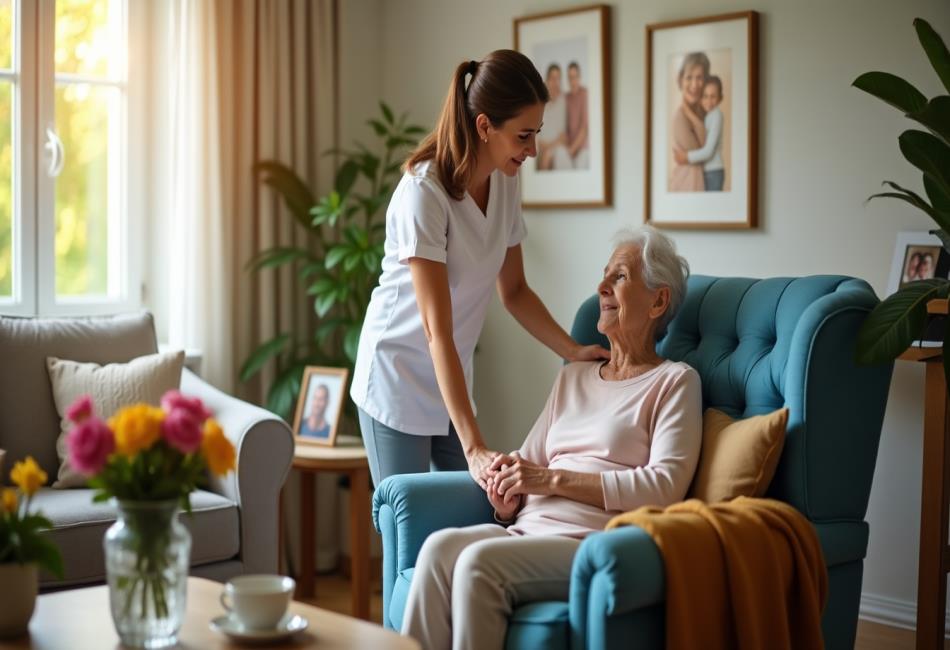
Live in care services provide personalized and flexible services that cater to various medical needs. Every individual has unique requirements in terms of assistance with everyday living or managing complicated health conditions. Care providers in live-in homes assess every person’s individual situation in order to provide the best level of care. For older people, homes for seniors, care can be tailored to offer comfort and help. Caregivers living in the home help in tasks such as medication management mobility, medication administration, and personal care. This service lets individuals remain in their homes and receive the assistance they require to maintain their independence and wellbeing. The individual approach to live in care ensures the best result. When it comes to managing certain medical conditions, live in carers are essential. Whether it’s chronic illness, post-surgery recovery, dementia or any other, 24 hour live in assistance is available round-the-clock assistance. Make a search on the following website, if you’re looking for more details on live in care agencies uk.
Live in care companies cooperate with families as well as healthcare providers to develop plans for care. This ensures that the service offered is consistent with medical requirements and family expectations. For those in need of more intensive support, such as daily nurse care, live-in providers can provide specific services. The adaptability of live in care means that individuals can have a customized care plan that will best meet their individual needs as well as provide comfort in a familiar environment. The in-home care offered to elderly persons is essential for those who struggle with day-to-day tasks. A lot of elderly people appreciate living at home care. It provides support and companionship, as well as emotional and physical assistance. Caregivers who live in the home can help with bathing, dressing up, meal preparation and light housekeeping. This personalized care makes sure that the elderly individual’s daily needs are met, increasing their mental and physical health. Furthermore, having a live in-home caregiver provides families with assurance that they are in good care. Caregiver is able to provide the physical aid and emotional support that is extremely valuable. 24-hour home care is a possibility for those with more challenging needs, making sure that assistance is always available.
Be it managing medications or providing comfort during the late hours, live in caregivers provide continuous care. Live in care providers offer an excellent degree of flexibility, adapting their care schedules to meet the needs of the individual. For individuals with physical disabilities or health conditions that require constant monitoring, 24 hour live in care is a vital service. It guarantees that medical attention is accessible at any time increasing the quality of your life and giving peace of head for families. In conclusion, live-in care services play a crucial job in ensuring that clients receive care suited to their unique health needs. It doesn’t matter if it’s home care for elderly clients in medical care, daily assistance, live in caregivers provide the highest quality of care that is tailored to the particular needs of the client. Being able to access 24 hour live in care will allow individuals to remain at home with the comfort of their own home. Live in-care agencies are able to collaborate with families and create programs that cater to both health and personal needs, offering both emotional and physical support. Flexible, personalized care offered is crucial for ensuring the wellbeing of every person.